Ein Lernendes und Interoperables, Smartes Expertensystem für die pädiatrische Intensivmedizin
Abkürzung: ELISE
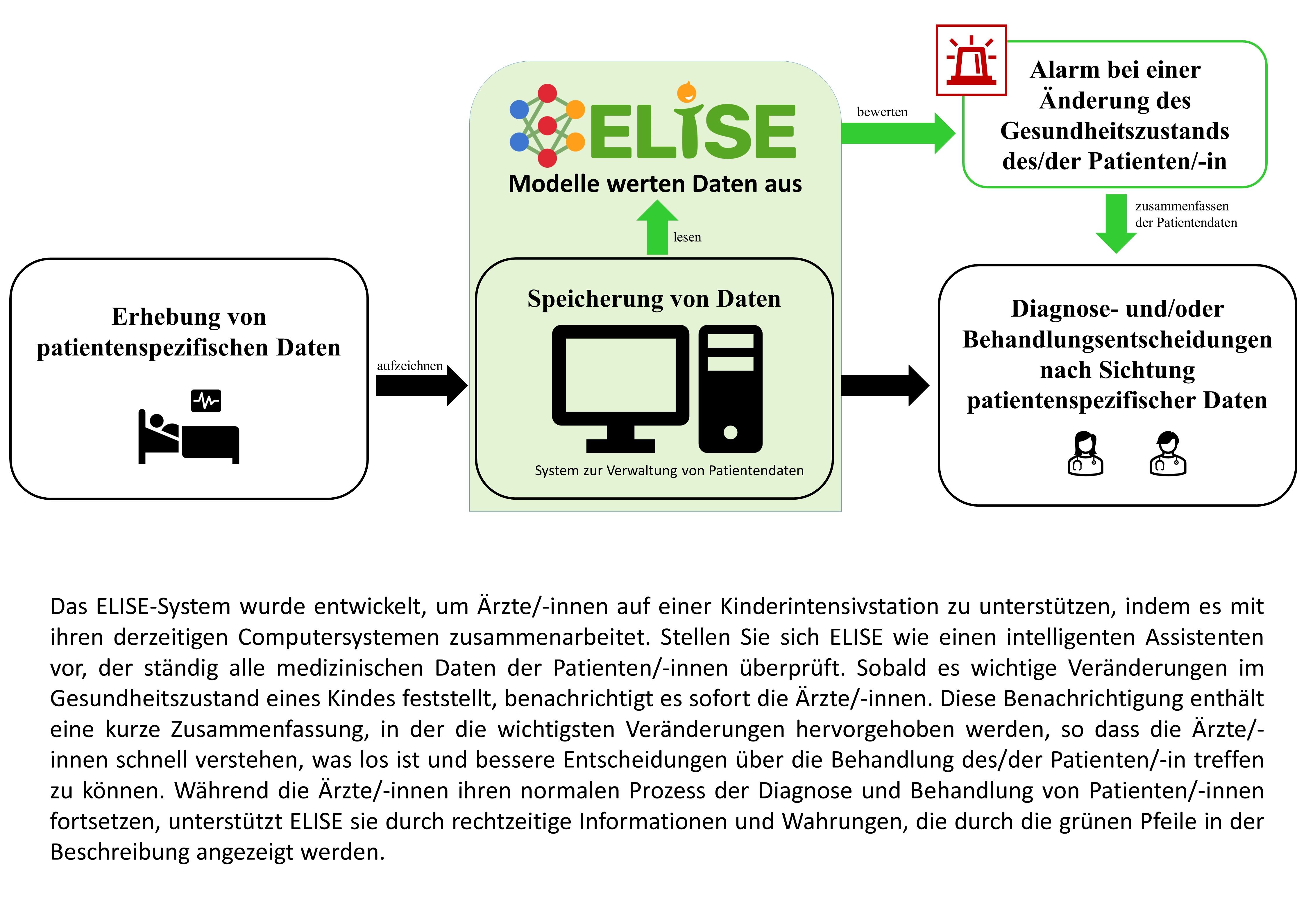
Das ELISE-Projekt widmet sich der Entwicklung eines digitalen klinischen Entscheidungsunterstützungssystems (CDSS) für die pädiatrische Intensivmedizin zur Optimierung von diagnostischen und therapeutischen Routineprozessen in der pädiatrischen Intensivmedizin. Gerade dort ist ein frühzeitiges Erkennen und Antizipieren von lebensbedrohlichen Erkrankungsprozessen entscheidend, denn die pädiatrische Intensivmedizin ist ein komplexer wissens- und erfahrungsbasierter Bereich, der das medizinische Personal kontinuierlich herausfordert. Alle diagnostischen und therapeutischen Maßnahmen sind aufgrund der altersspezifischen Entwicklungsstadien von Kindern und der heterogenen, teils seltenen Erkrankungen innerhalb dieser Patientenpopulation von sehr individuellen Variationen geprägt. Um diesen Herausforderungen zu begegnen, haben wir ELISE entwickelt, das Kliniker/-innen bei der frühzeitigen Erkennung des Systematischen Inflammatorischen Response-Syndroms (SIRS), der Sepsis und den damit verbundenen Organdysfunktionen (d.h. hepatische/ hämatologische/ respiratorische/ renale/ kardiovaskuläre Organdysfunktion) unterstützen kann.
Das ELISE CDSS besteht aus mehreren, zielzustandsspezifischen, wissensbasierten Erkennungsmodellen und datengetriebenen Vorhersagemodellen. Diese Modelle werden entwickelt und auf ihre diagnostische Genauigkeit (d. h. gemessen an Sensitivität und Spezifität) geprüft, bevor sie validiert werden. Sobald sie eine akzeptabel hohe Genauigkeit bei der Erkennung und/oder Vorhersage von diagnostischen Ereignissen erreicht haben, können diese Modelle in eine Routineanwendung des CDSS für die pädiatrische Intensivmedizin integriert werden.
Veröffentlichung in Zeitschriften
Das, P., Wiese, L., Mast, M., Boehnke, J., Wulff, A., Marschollek, M., Bode, L., Rathert, H., Jack, T., Schamer, S., Beerbaum, P., Rübsamen, N., Karch, A., Groszweski-Anders, C., Haller, A., & Frank, T. (2024). An attention-based bidirectional LSTM-CNN architecture for the early prediction of sepsis. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41060-024-00568-z
Böhnke, J., Zapf, A., Kramer, K., Weber, P., ELISE Study Group, Karch, A., & Rübsamen, N. (2024). Diagnostic test accuracy in longitudinal study settings: theoretical approaches with use cases from clinical practice. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 169, 111314. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2024.111314
Das, P. P., Mast, M., Wiese, L., Jack, T., & Wulff, A. (2024). Algorithmic Fairness in Healthcare Data with Weighted Loss and Adversarial Learning. In Intelligent Systems and Application, ed. Kohei Arai. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 264-83. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47715-7_18
Bode, L., Mast, M., Rathert, H., Elise Study Group, Jack, T., & Wulff, A. (2023). Achieving Interoperable Datasets in Pediatrics: A Data Integration Approach. Studies in health technology and informatics, 305, 327–330. https://doi.org/10.3233/SHTI230496
Tute, E., Mast, M., & Wulff, A. (2023). Targeted Data Quality Analysis for a Clinical Decision Support System for SIRS Detection in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients. Methods of information in medicine, 62(S 01), e1–e9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1760238
Das, P. P., Wiese, L., and ELISE Study Group. (2023). Explainability Based on Feature Importance for Better Comprehension of Machine Learning in Healthcare. In New trends in Database and Information Systems, eds. Alberto Abelló, Panos Vassiliadis, Oscar Romero, Robert Wrembel, Francesca Bugiotti, Johann Gamper, Genoveva Vargas Solar, and Ester Zumpano. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 324–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42941-5_28
Wulff, A., Bode, L., Mast. M. (2022), Ein wissensbasiertes, interoperables Entscheidungsunterstützungssystem für die pädiatrische Intensivmedizin. mdi medizin://dokumentation/informatik/informationsmanagement/. 2022;3:85-87. German.
Böhnke, J., Rübsamen, N., Mast, M., Rathert, H., ELISE Study Group, Karch, A., Jack, T., & Wulff, A. (2022). Prediction models for SIRS, sepsis and associated organ dysfunctions in paediatric intensive care: study protocol for a diagnostic test accuracy study. BMJ paediatrics open, 6(1), e001618. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjpo-2022-001618
Wulff, A., Mast, M., Bode, L., Rathert, H., Jack, T., & Elise Study Group (2022). Towards an Evolutionary Open Pediatric Intensive Care Dataset in the ELISE Project. Studies in health technology and informatics, 295, 100–103. https://doi.org/10.3233/SHTI220670
Böhnke, J., Varghese, J., ELISE Study Group, Karch, A., & Rübsamen, N. (2022). Systematic review identifies deficiencies in reporting of diagnostic test accuracy among clinical decision support systems. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 151, 171–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.08.003
Wulff, A., Mast, M., Bode, L., Marschollek, M., Schamer, S., Beerbaum, P., Rübsamen, N., Böhnke, J., Karch, A., Das, P. P., Wiese, L., Groszewski-Anders, C., Haller, A., Frank, T., Rathert, H., & Jack, T. (2022). ELISE - An open pediatric intensive care data set [Data set]. https://leopard.tu-braunschweig.de/receive/dbbs_mods_00070468
Bode, L., Schamer, S., Böhnke, J., Bott, O. J., Marschollek, M., Jack, T., Wulff, A., & ELISE Study Group (2022). Tracing the Progression of Sepsis in Critically Ill Children: Clinical Decision Support for Detection of Hematologic Dysfunction. Applied clinical informatics, 13(5), 1002–1014. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1950-9637
Mast, M., Marschollek, M., Jack, T., Wulff, A., & Elise Study Group (2022). Developing a Data Driven Approach for Early Detection of SIRS in Pediatric Intensive Care Using Automatically Labeled Training Data. Studies in health technology and informatics, 289, 228–231. https://doi.org/10.3233/SHTI210901
Konferenzbeiträge/-abstracts
Wachenbrunner J, Mast M, Böhnke J, Bode L, Rübsamen N, Rathert H, et al. Developing a Complex Rule-Based Clinical Decision Support System for Detection of Acute Kidney Injury after Pediatric Cardiac Surgery. In: The Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgeon [Internet]. Georg Thieme Verlag KG; 2024 [cited 2024 Feb 26]. p. DGPK-V04. Available from: http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0044-1780717
Böhnke J, Zapf A, Kramer K, Weber P, Karch A, Rübsamen N. Methods for estimation of diagnostic test accuracy using longitudinal data. In German Medical Science GMS Publishing House; 2023. p. DocAbstr. 162. Available from: https://www.egms.de/static/en/meetings/gmds2023/23gmds056.shtml
Das PP, Mast M, Wiese L, Jack T, Wulf A. Data Extraction for Associative Classification using Mined Rules in Pediatric Intensive Care Data. In Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V.; 2023 [cited 2024 Apr 26]. p. 981–94. Available from: https://dl.gi.de/handle/20.500.12116/40376
Jack, T., Wulff, A., Rathert, H., Montag, S., Marschollek, M., & Beerbaum, P. (2022). Development of a Clinical Decision Support System for the Detection of SIRS after Surgery for Congenital Heart Disease. The Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgeon, 70(S 2), DGPK-V36. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1742994
Böhnke J, Varghese J, Karch A, Rübsamen N. Reporting quality and risk of bias in studies evaluating the diagnostic test accuracy of clinical decision support systems: a systematic review of current practice. In German Medical Science GMS Publishing House; 2022. p. DocAbstr. 81. Available from: https://www.egms.de/static/en/meetings/gmds2022/22gmds006.shtml
Projektdetails
Verantwortliche Personen
Projektleiter am IESM
Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. André Karch, MD
Projektlaufzeit
Okt 2020 - Dez 2023
Kooperationspartner
Bioinformatik und Digital Health, Fraunhofer ITEM (Entwickler/-innen der datengetriebenen Vorhersagemodelle)
Medisite GmbH (Softwareentwickler/-innen)
Pädiatrische Kardiologie und Pädiatrische Intensivmedizin, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover (Kliniker/-innen und Datenbereitsteller/-innen)
Institut für Medizinische Informatik, Peter L. Reichertz Institut (Entwickler/-innen der wissensbasieren Erkennungsmodelle und der datengetriebenen Vorhersagemodelle)
Institut für Epidemiologie und Sozialmedizin, Universität Münster (Epidemiologen/-innen)
Förderung
Bundesministerium für Gesundheit
Förderkennzeichen: 2520DAT66C
Förderungszeitraum: Oktober 2020 – Dezember 2023 (Analysen sind noch nicht abgeschlossen)
Preise
Externe Links
Das, P., Wiese, L., Mast, M., Boehnke, J., Wulff, A., Marschollek, M., Bode, L., Rathert, H., Jack, T., Schamer, S., Beerbaum, P., Rübsamen, N., Karch, A., Groszweski-Anders, C., Haller, A., & Frank, T. (2024). An attention-based bidirectional LSTM-CNN architecture for the early prediction of sepsis. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41060-024-00568-z
Böhnke, J., Zapf, A., Kramer, K., Weber, P., ELISE Study Group, Karch, A., & Rübsamen, N. (2024). Diagnostic test accuracy in longitudinal study settings: theoretical approaches with use cases from clinical practice. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 169, 111314. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2024.111314
Das, P. P., Mast, M., Wiese, L., Jack, T., & Wulff, A. (2024). Algorithmic Fairness in Healthcare Data with Weighted Loss and Adversarial Learning. In Intelligent Systems and Application, ed. Kohei Arai. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 264-83. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47715-7_18
Bode, L., Mast, M., Rathert, H., Elise Study Group, Jack, T., & Wulff, A. (2023). Achieving Interoperable Datasets in Pediatrics: A Data Integration Approach. Studies in health technology and informatics, 305, 327–330. https://doi.org/10.3233/SHTI230496
Tute, E., Mast, M., & Wulff, A. (2023). Targeted Data Quality Analysis for a Clinical Decision Support System for SIRS Detection in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients. Methods of information in medicine, 62(S 01), e1–e9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1760238
Das, P. P., Wiese, L., and ELISE Study Group. (2023). Explainability Based on Feature Importance for Better Comprehension of Machine Learning in Healthcare. In New trends in Database and Information Systems, eds. Alberto Abelló, Panos Vassiliadis, Oscar Romero, Robert Wrembel, Francesca Bugiotti, Johann Gamper, Genoveva Vargas Solar, and Ester Zumpano. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 324–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42941-5_28
Wulff, A., Bode, L., Mast. M. (2022), Ein wissensbasiertes, interoperables Entscheidungsunterstützungssystem für die pädiatrische Intensivmedizin. mdi medizin://dokumentation/informatik/informationsmanagement/. 2022;3:85-87. German.
Böhnke, J., Rübsamen, N., Mast, M., Rathert, H., ELISE Study Group, Karch, A., Jack, T., & Wulff, A. (2022). Prediction models for SIRS, sepsis and associated organ dysfunctions in paediatric intensive care: study protocol for a diagnostic test accuracy study. BMJ paediatrics open, 6(1), e001618. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjpo-2022-001618
Wulff, A., Mast, M., Bode, L., Rathert, H., Jack, T., & Elise Study Group (2022). Towards an Evolutionary Open Pediatric Intensive Care Dataset in the ELISE Project. Studies in health technology and informatics, 295, 100–103. https://doi.org/10.3233/SHTI220670
Böhnke, J., Varghese, J., ELISE Study Group, Karch, A., & Rübsamen, N. (2022). Systematic review identifies deficiencies in reporting of diagnostic test accuracy among clinical